Copilot for process discovery and process performance insights
Navigating across process mining visualizations to extract insights for improvement is often very time-consuming. To enable a faster and more convenient approach to process discovery, we have an AI-powered Copilot.
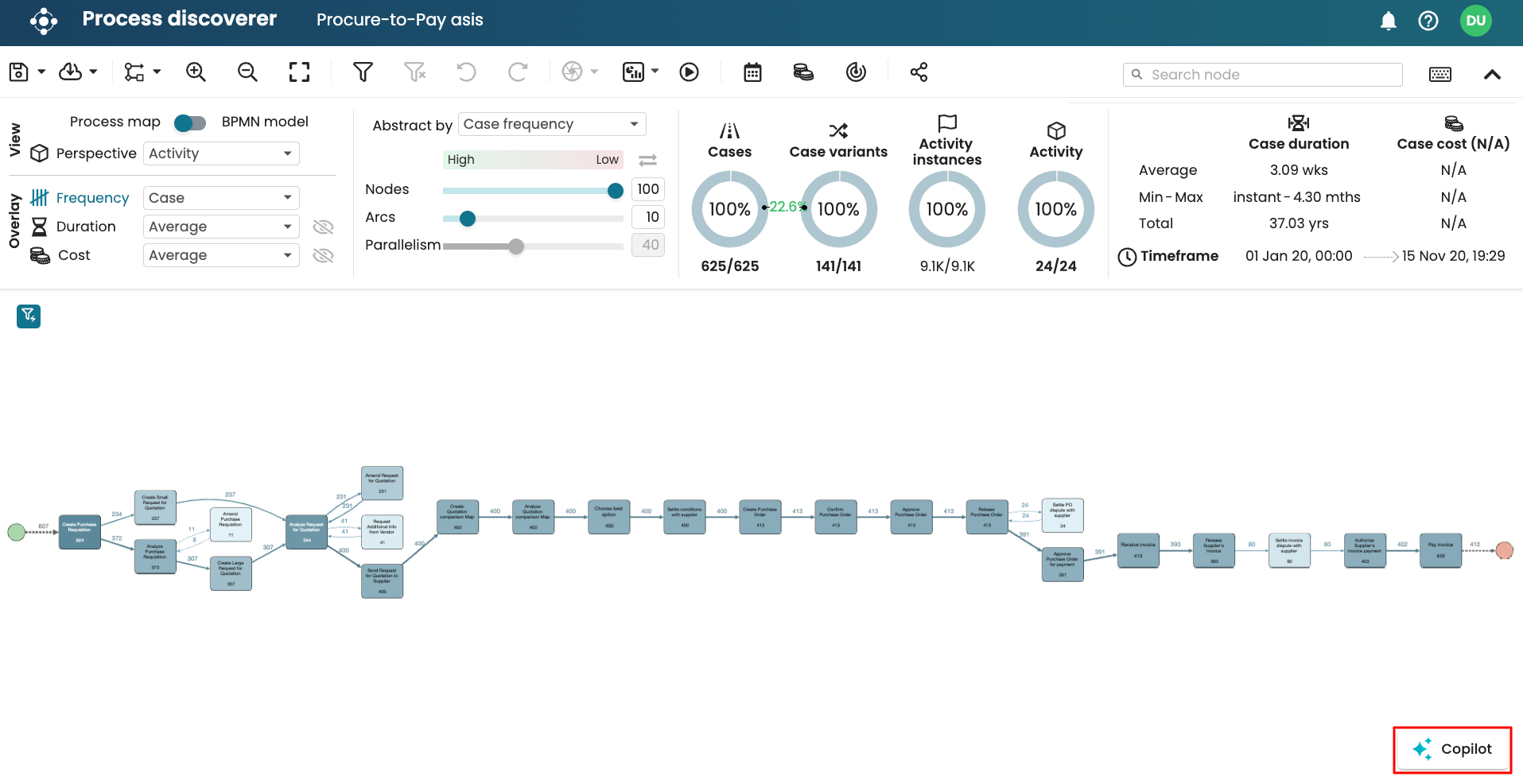
Copilot is a chat interface that allows us to ask process discovery questions in Process Discoverer. The chat conversation is based on the process map displayed in Process Discoverer and can answer quick questions about the process performance. So, rather than navigating the barrage of information in Process Discoverer, we can simply ask Apromore.
To use our AI Copilot, open an event log in Process Discoverer and click Copilot.
This opens the Copilot chat window. We see examples of questions we can ask.
Ask process discovery questions
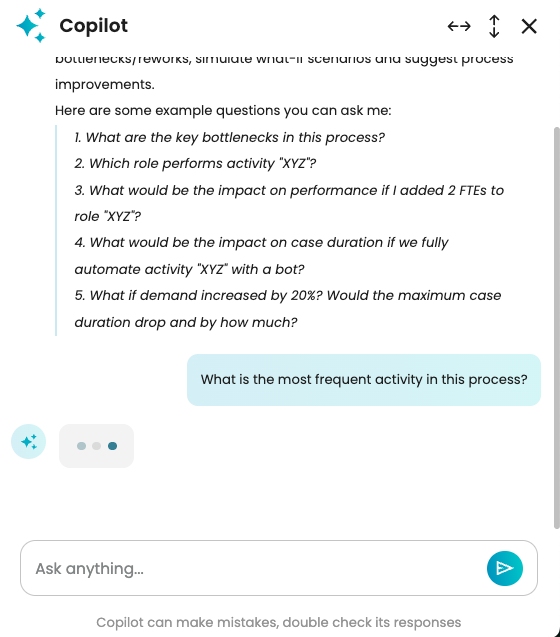
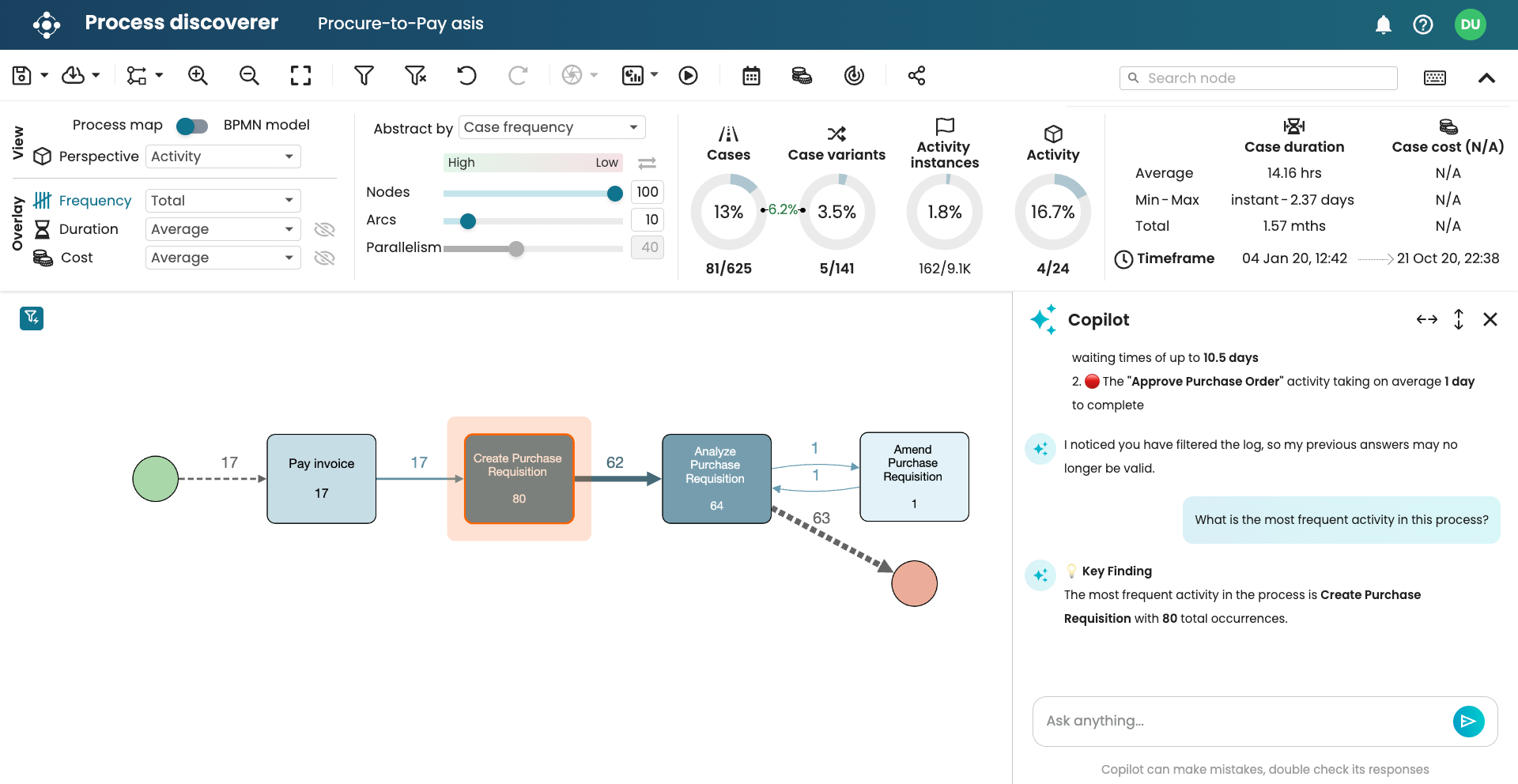
In the chat input field, we can ask process discovery questions about the event log we have opened. For instance, we can ask: What is the most frequent activity in this process? Press Enter.
We see a progress bar indicating that Copilot is finding the answer to our question.
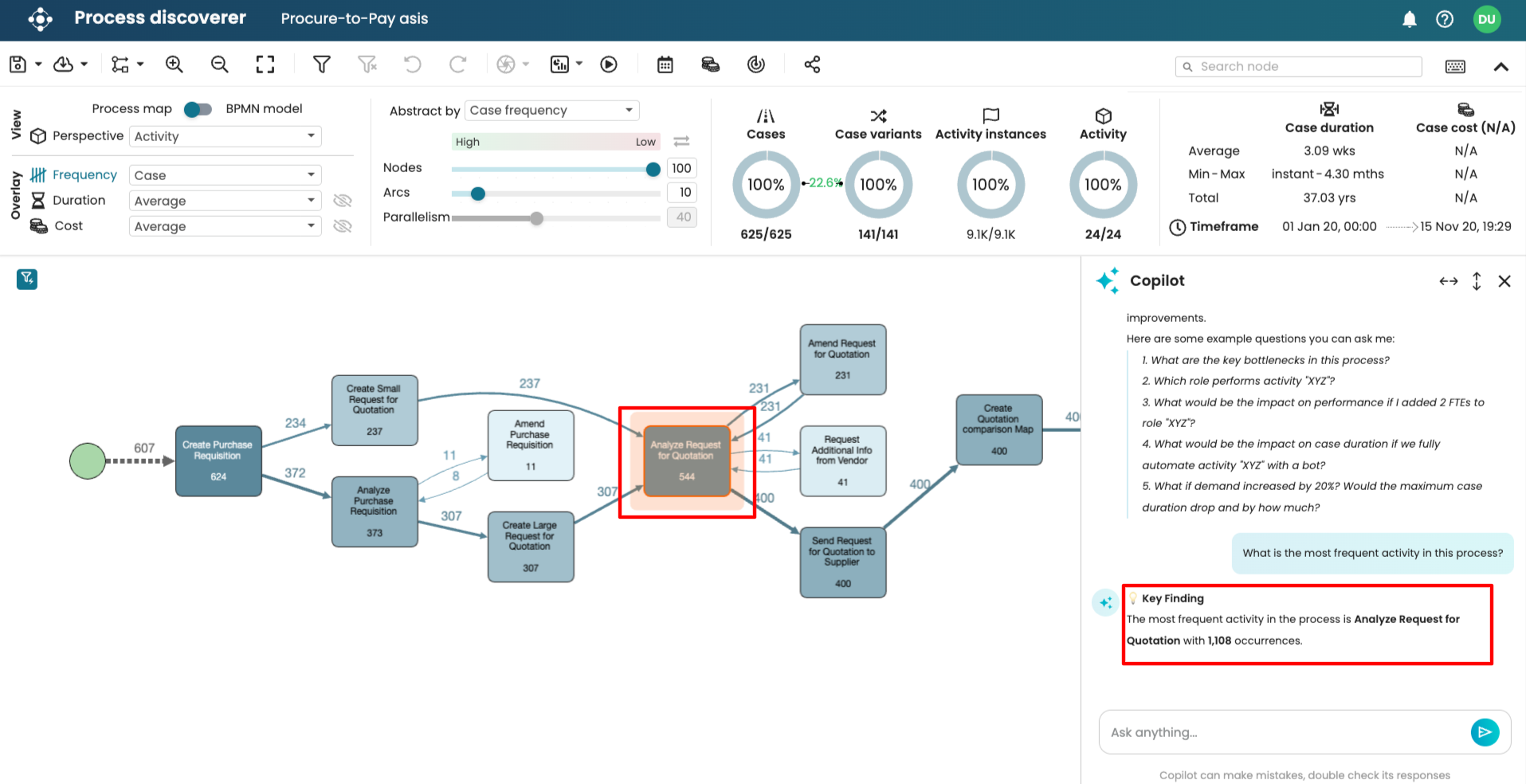
After a few seconds, Copilot returns the answer. For easy discovery, when Copilot returns answers that involve activities in the process map, Copilot highlights the activities involved.
Note
By default, Copilot is disabled in client instances. To turn on Copilot in your tenancy, please contact your account executive or customer support. Once enabled, Copilot enables the user to submit up to 50 prompts per calendar.
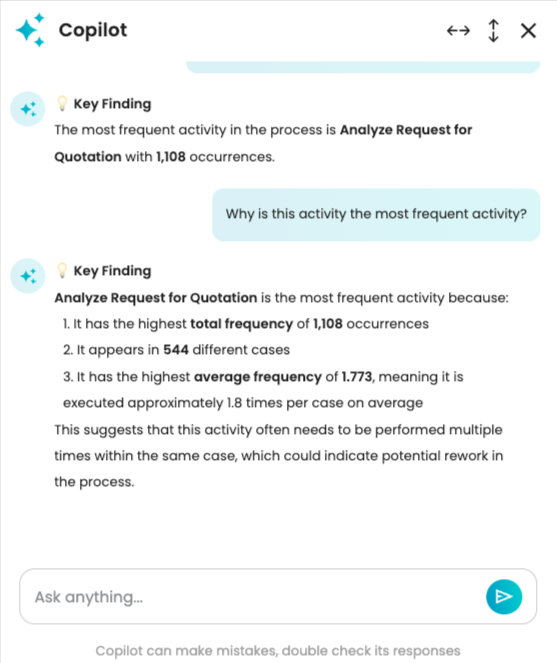
To enable us to easily identify answers, Copilot responds directly and concisely. We can however ask questions to dig deeper. For instance, we can ask why this activity is the most frequent.
The chatbot tells us it has the highest total frequency of 1108, which is correct.
Note
AI models are non-deterministic. Hence, given the same prompt, the model may return a different response.
Copilot understands the context based on the chat history in a session. Notice that we did not specify the activity in question in the second prompt, but Copilot correctly determined it from our earlier prompt. We can clear the chat history by closing and reopening Copilot or refreshing the Process Discoverer page.
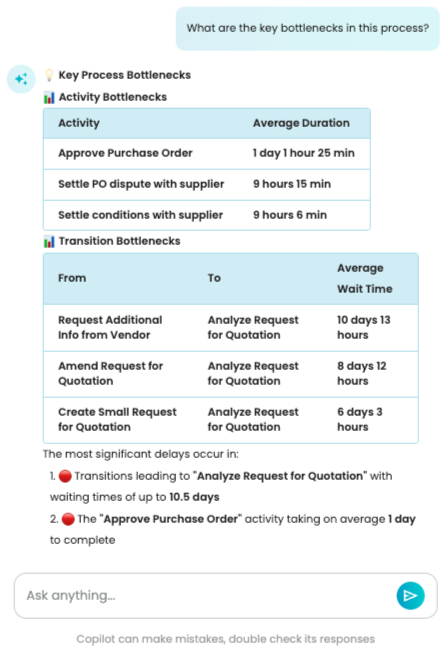
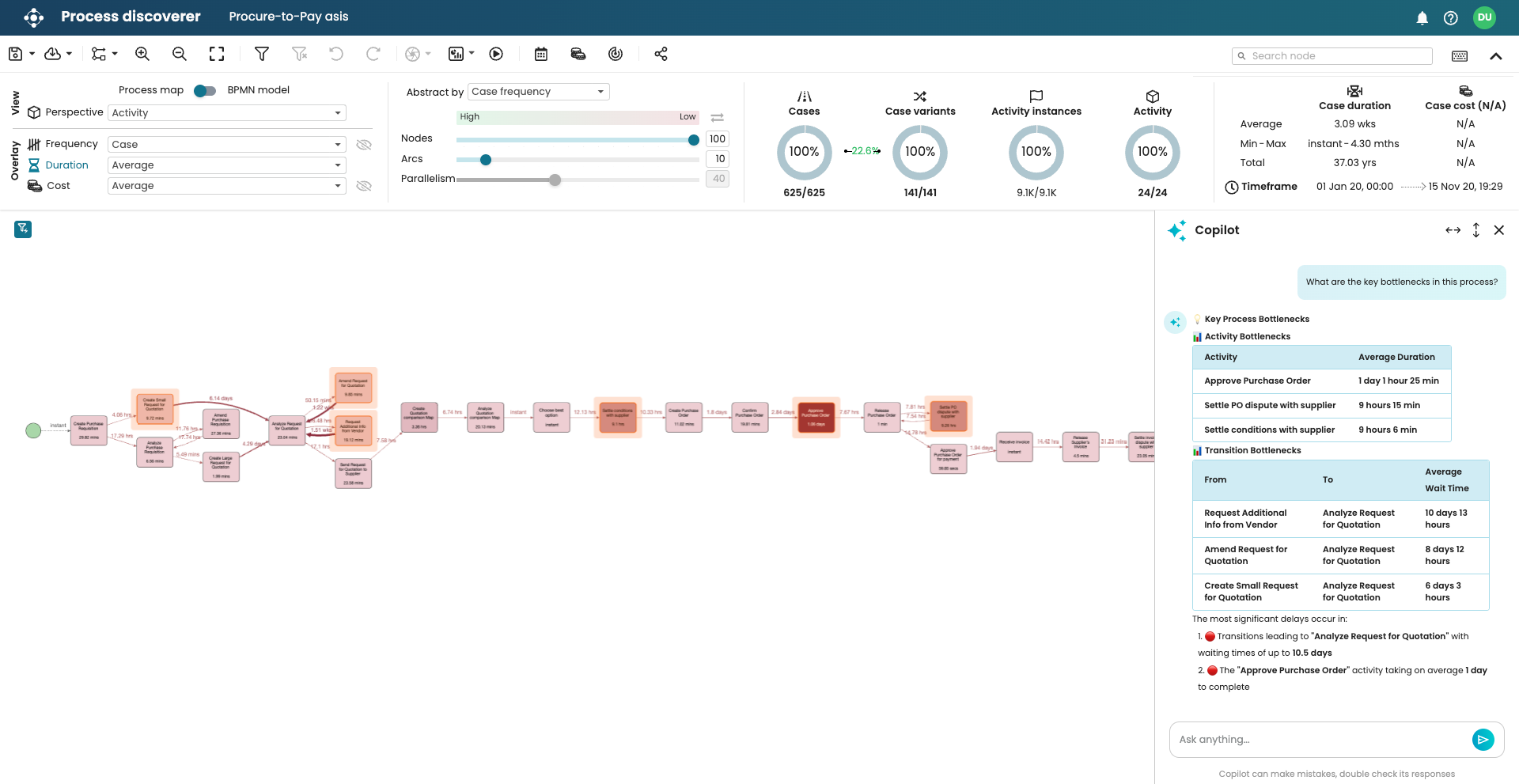
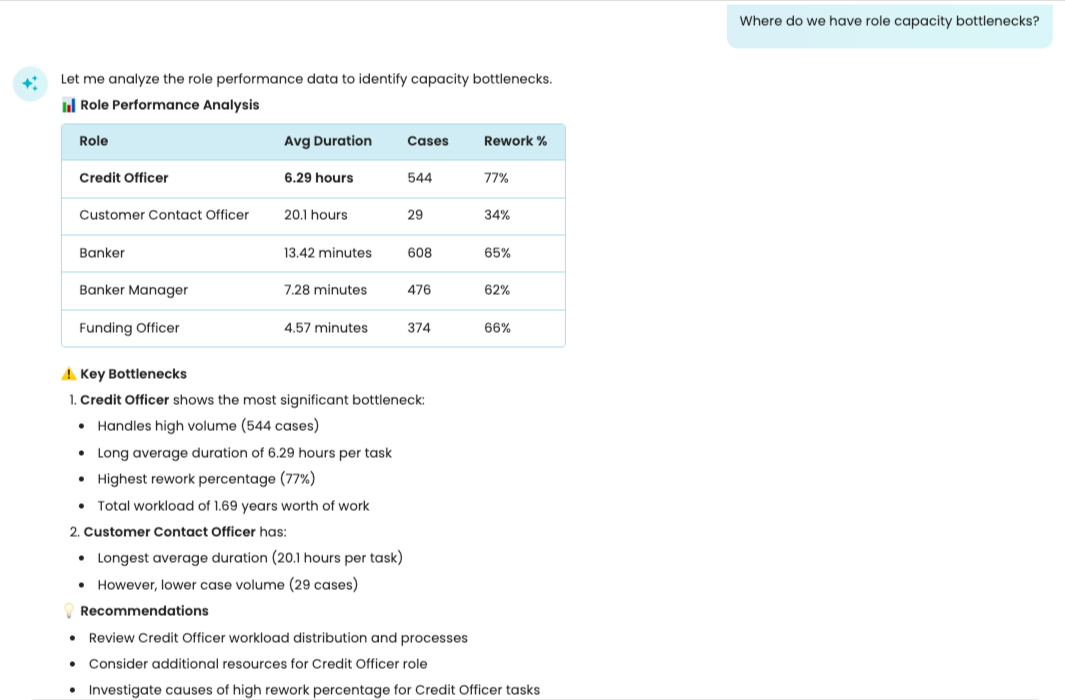
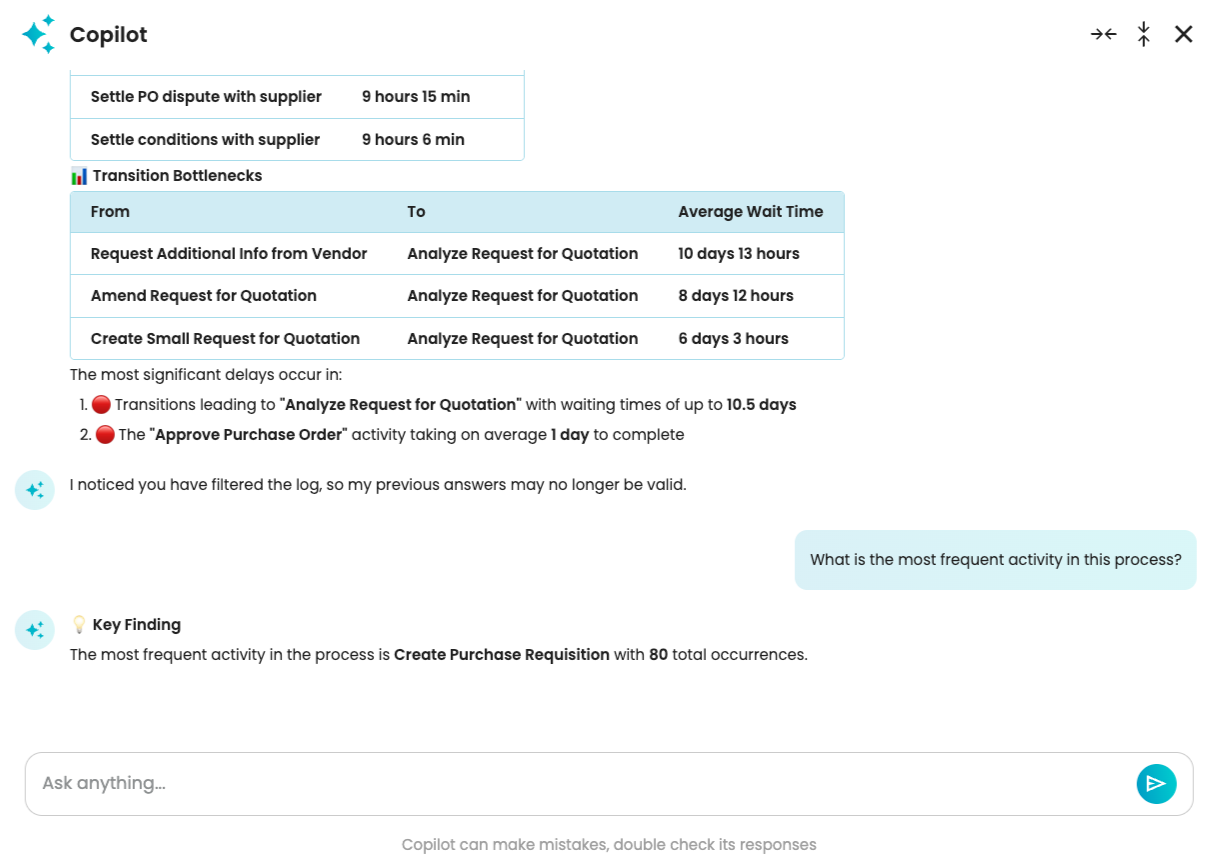
Let’s ask Copilot to determine the bottlenecks in the process.
Copilot correctly identifies the activity and transition bottlenecks.
Note
When multiple activities are referenced, they are all highlighted.
As seen, all bottleneck activities are highlighted.
When a response contains multiple strings, we decide which elements to highlight using a two-step approach:
Exact Match: We first look for an element that exactly matches the response string.
Example: If the Copilot response is “Banker Manager” and a process map node with the same name exists, it will be highlighted.
Substring Match: If no exact match is found, we check for substrings of the response.
Example: If the Copilot response is “Banker Manager” and nodes named “Banker” and “Manager” exist, both will be highlighted.
In summary, we prioritize exact matches over substrings and longer phrases over shorter ones.
Note
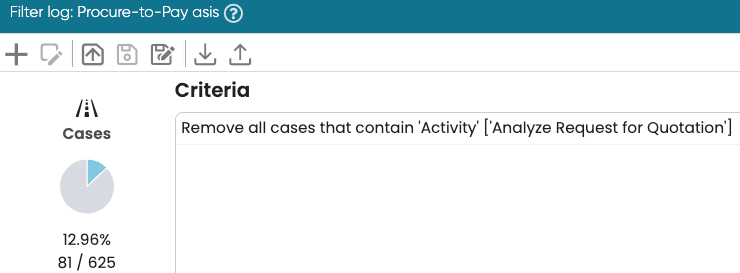
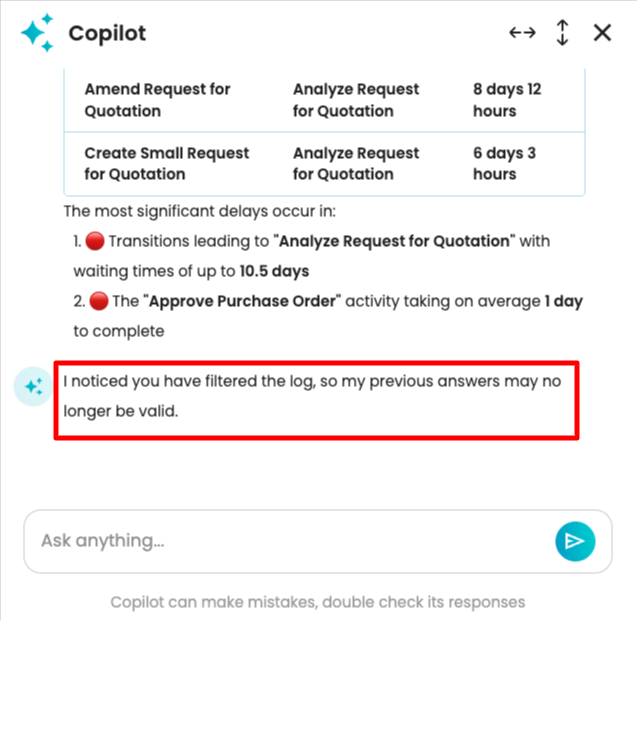
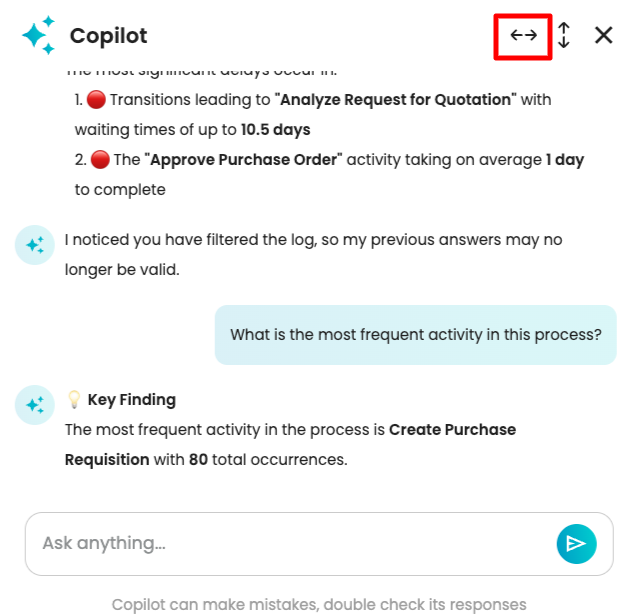
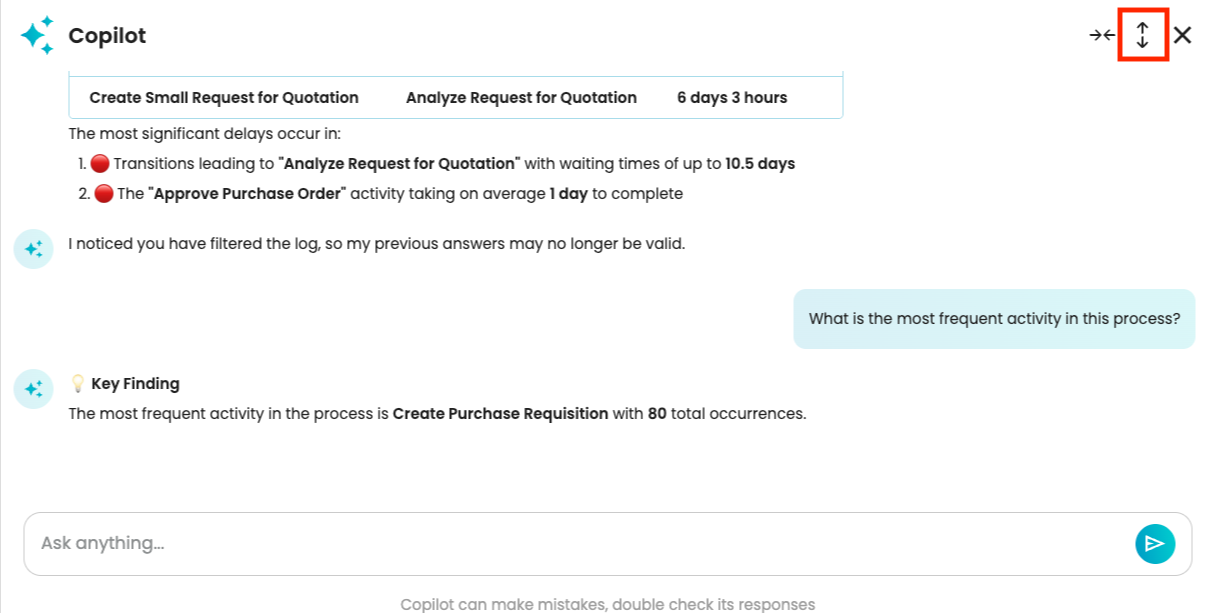
When we apply a filter to the log, answers from Copilot will be based on the filtered process map. To demonstrate this, let us remove the most frequent activity, “Analyze Request for Quotation”.
Copilot detects that a filter has been applied and informs us that previous answers may no longer be valid.
Now, let us ask what the most frequent activity in the process is.
Copilot provided its answer based on the currently displayed filtered log.
Ask questions about filtered processes
We can answer process discovery questions that involve the use of filters.
Note
Copilot can only answer questions that involve the use of case attributes and timeframe filters.
Ask questions involving case attribute filters
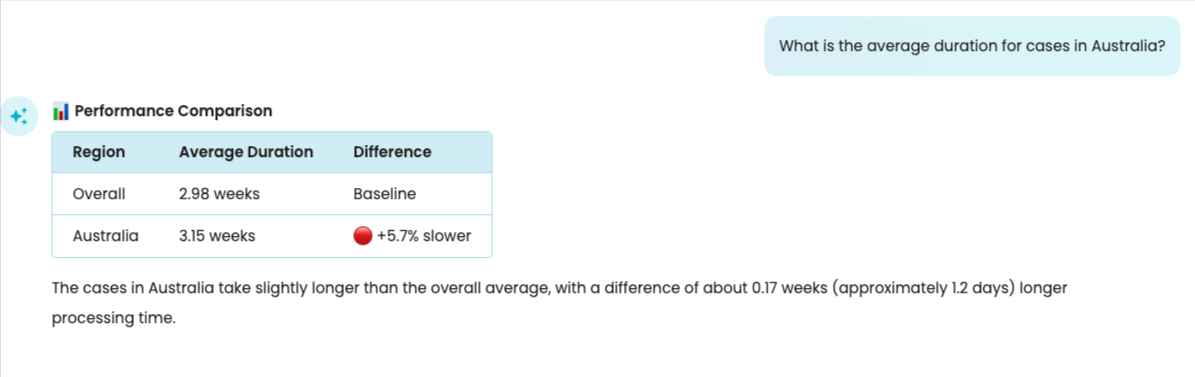
We can ask: What is the average duration for cases in Australia?
Copilot will create the attribute filter in the background and return its answer based on the filtered log. It also compares the result to the baseline.
Note
We do not need to enter attribute names exactly as they appear in the log. Our Copilot intelligently interprets what you mean and infers the correct attribute to filter by. For example, if a country attribute value is “AUS” in the log, Copilot understands that this means “Australia.”
We can include only 10 filters in a single prompt.
We cannot ask questions about attributes that contain more than 50 distinct values.
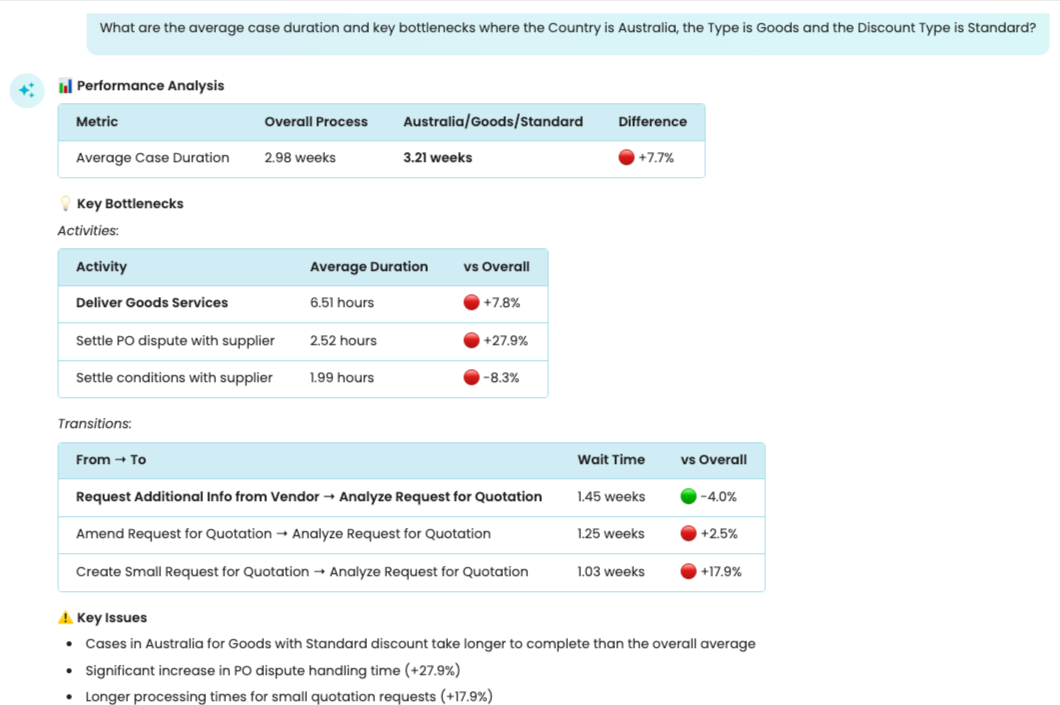
We can also ask more complex questions that would require the combination of multiple filters. For instance, we can ask: What are the average case duration and key bottlenecks where the Country is Australia, the Type is Goods, and the Discount Type is Standard?
In the background, Copilot creates a filter that retains cases where:
Country is “AUS”.
Type is “Goods” and
Discount_Type is “Standard”.
It then compares the filter results with the baseline log (unfiltered log).
Copilot is also aware of roles and their capacity within a process. For example, we can ask: Where do we have role capacity bottlenecks?
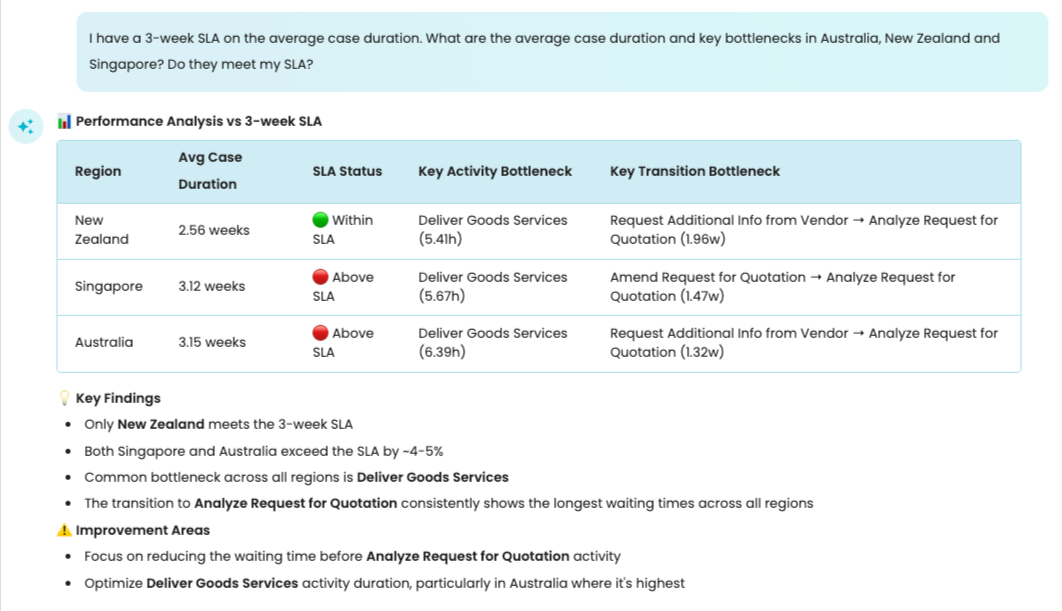
We can also give Copilot context about our SLA and have it answer questions based on our SLA status. For instance, we can ask: I have a 3-week SLA on the average case duration. What are the average case duration and key bottlenecks in Australia, New Zealand, and Singapore? Did they meet my SLA?
Copilot created three separate filters before answering the question. It also tells us which region fulfilled our SLA and the ones that did not. It also points us to the key bottlenecks in all three regions.
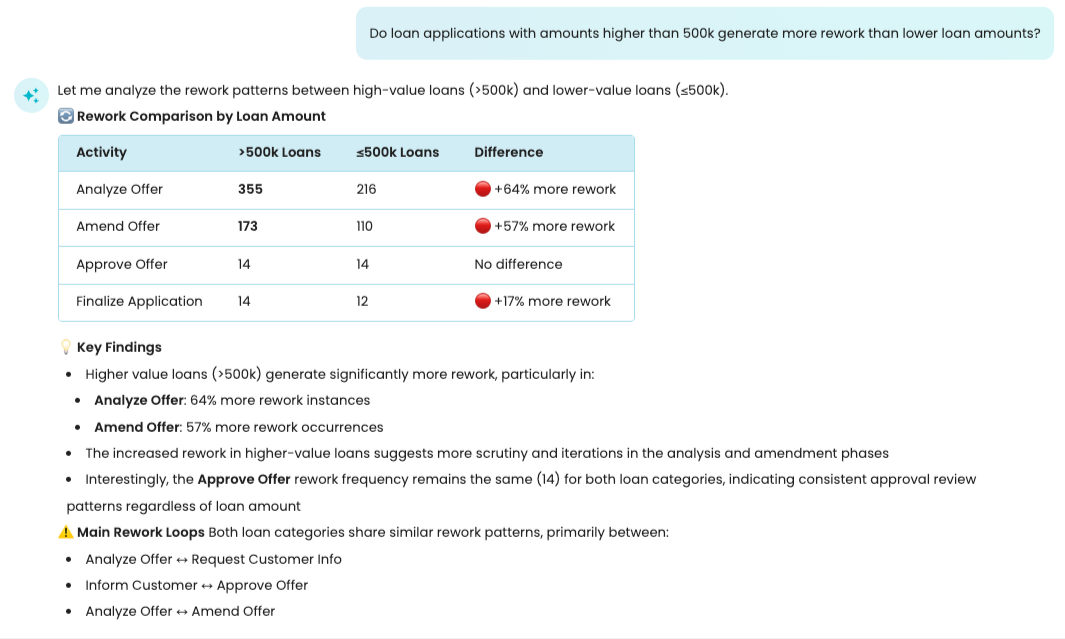
We can also ask questions involving numeric attributes. For example, we can ask: Do loan applications with amounts higher than 500k generate more rework than lower loan amounts?
Ask questions involving timeframe filters
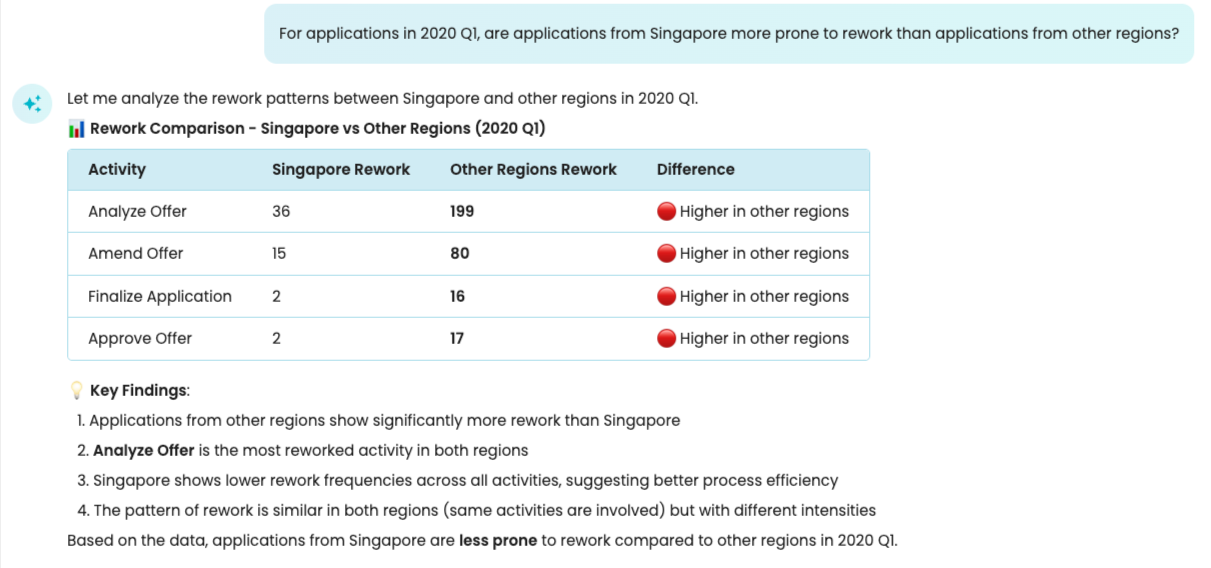
For the use of timeframe filters, we can ask: For applications in 2020 Q1, are applications from Singapore more prone to rework than applications from other regions?
In the background, Copilot creates the timeframe filter that retains cases in Q1 of 2020. It then answers the question based on the filtered log results.
Ask questions about process comparison
We can also ask questions that would require Copilot to compare variants of the process. Imagine we wish to see whether the loan application purpose affects the time to loan payment.
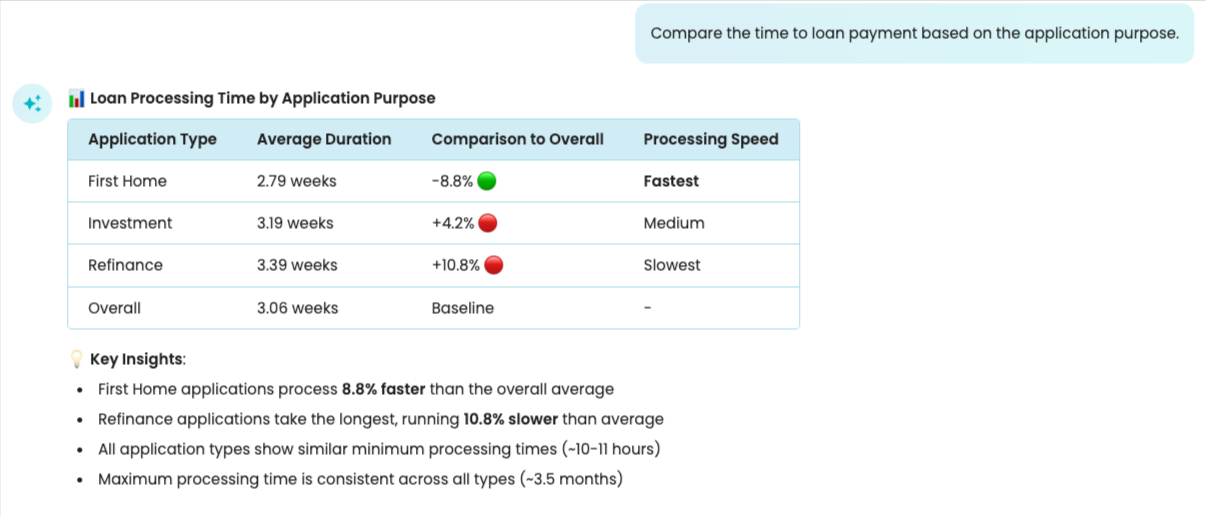
Let us ask: Compare the time to loan payment based on the application purpose.
Copilot creates multiple variants based on the application purpose and compares the time to loan payment for each variant.
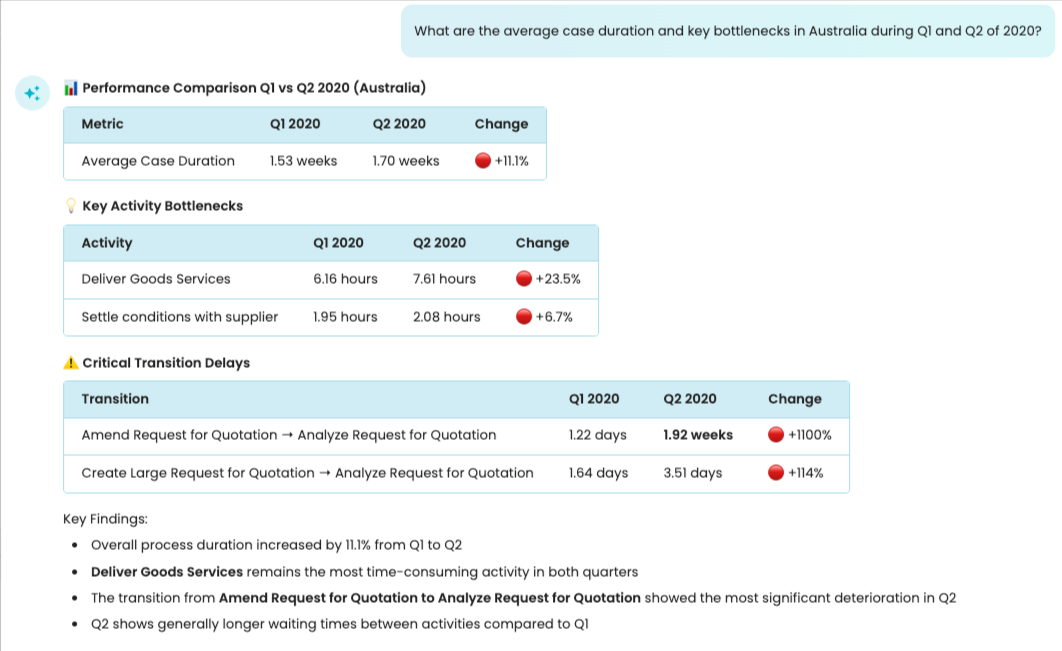
We can also combine the use of attributes and timeframe filters in a comparative analysis. For instance, we can ask: What are the average case duration and key bottlenecks in Australia during Q1 and Q2 of 2020?
Copilot first creates a filter where the country is AUS. Then create two filter variations – in the first, retain cases in Q1, and in the second, retain cases in Q2. It then answers the question based on the filtered logs.
Change Copilot window size
We can expand or contract Copilot’s window. We can choose to expand it horizontally or vertically. To expand horizontally, click the horizontal expand icon.
This increases the window width.
To expand vertically, click the vertical expand icon.
And this expands the Copilot window vertically.
Similarly, we can contract the window horizontally or vertically by clicking the respective contract icon.
We can close the Copilot window by clicking the close icon.
Note
When using Copilot, the chat history is retained even when the chat window is closed, or Process Discoverer is refreshed. To clear the chat history, reopen the event log.